Imagine gazing up at the night sky, a canvas of twinkling lights, each a celestial beacon with its own story to tell. Have you ever wondered about the secrets hidden within those stellar diamonds? What are their origins, their lives, and their eventual fates? The universe, a cosmic laboratory, unfolds an extraordinary saga in the life cycle of stars – a breathtaking dance of creation, transformation, and ultimate demise. This journey, from humble beginnings to spectacular endings, is a testament to the intricate workings of nature’s grand design. This article will be your guide, delving into the intricate details of the life cycle of a star with an emphasis on the answers to common worksheet questions.
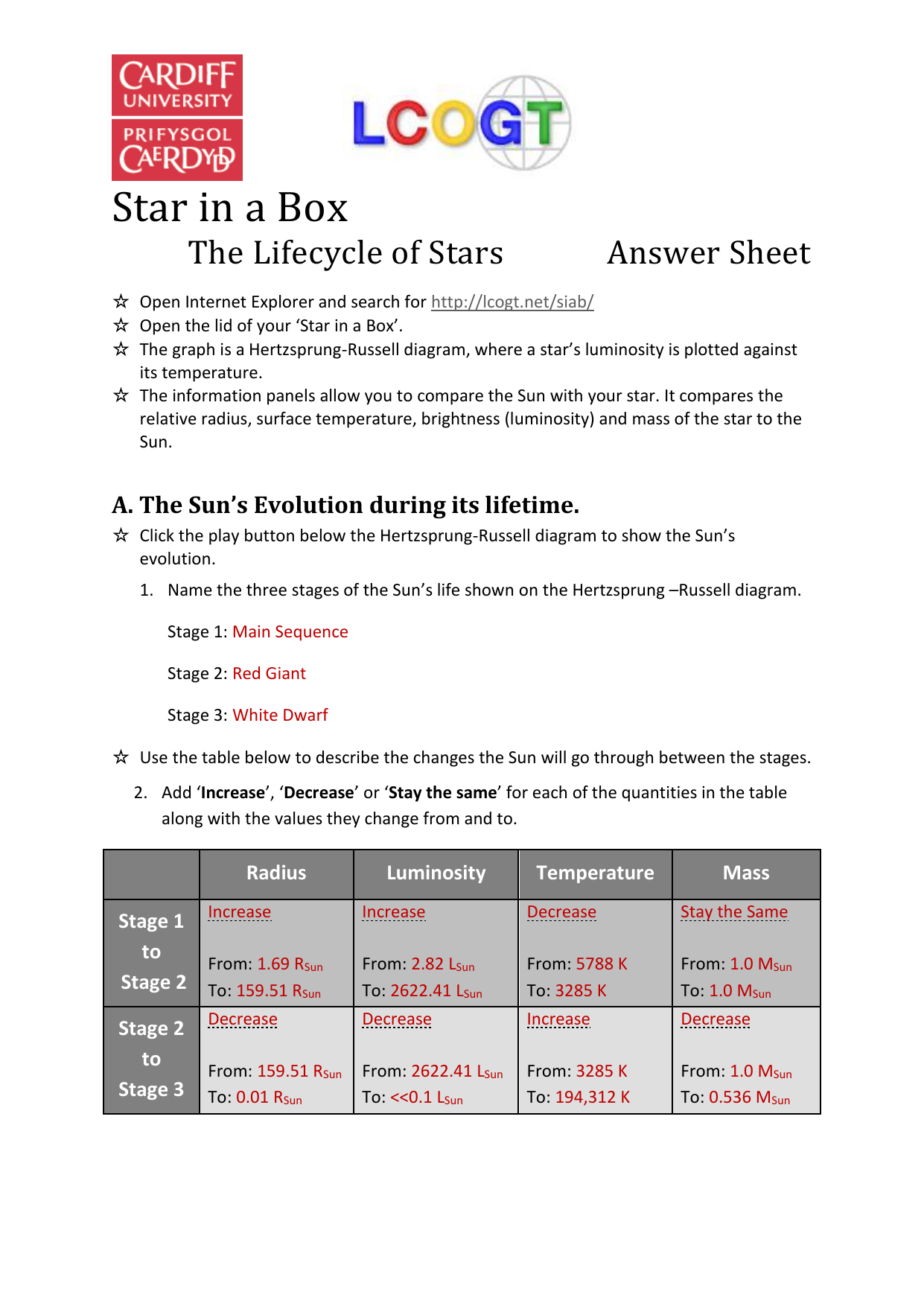
Image: materialmediaburger.z21.web.core.windows.net
The life cycle of a star is a captivating journey that begins with the collapse of a vast cloud of interstellar gas and dust. These clouds, called nebulae, are the nurseries of stars, where the raw materials of the cosmos are sculpted into celestial masterpieces. As gravity pulls these particles together, the cloud begins to spin, progressively heating up and increasing in density. This process can take millions of years, but eventually, the core of the collapsing nebula reaches a critical temperature, igniting the nuclear furnace that powers a star’s life. This event marks the birth of a star, a magnificent moment of cosmic fire. With newfound energy, the star pushes back against the crushing force of gravity, finding a delicate balance that allows it to shine for billions of years.
The Stellar Nursery: Birth of a Star
Worksheet Question: Explain the process that leads to the formation of a star.
Answer: Stars are born from immense clouds of gas and dust known as nebulae. These clouds are composed primarily of hydrogen and helium, the most abundant elements in the universe. Gravity plays a crucial role in stellar formation, attracting particles within the nebula towards each other. As the cloud collapses under its own gravity, its density increases, and the particles collide with greater frequency. This constant collision leads to a significant increase in temperature at the core of the nebula. When the temperature reaches a critical threshold, nuclear fusion ignites, releasing an immense amount of energy, and marking the birth of a star.
Worksheet Question: What are the main elements found in a nebula?
Answer: The principal elements present in nebulae are hydrogen and helium. These elements, along with trace amounts of other lighter elements, comprise the raw materials that fuel the nuclear reactions within stars.
The Stellar Engine: Fusion Powering the Star
Worksheet Question: What is the process of nuclear fusion, and how does it power a star?
Answer: Nuclear fusion is the engine that drives a star’s life. At the star’s core, immense pressure and temperature force hydrogen atoms to collide with such force that their nuclei fuse together, creating helium atoms. This process releases an enormous amount of energy in the form of light and heat, which is what we see as the star’s brilliance. This fusion reaction is akin to the controlled explosion of a hydrogen bomb, but on a much grander and more continuous scale.
Worksheet Question: What is the role of gravity in the life of a star?
Answer: Gravity plays a vital role in a star’s life. While it is the force that initiates the star’s formation, it also determines the star’s stability. The inward pull of gravity is balanced by the outward pressure generated by the heat of nuclear fusion. This delicate equilibrium is critical to a star’s existence. If gravity were to overwhelm the outward pressure, the star would collapse under its own weight.
The Stellar Life Cycle: From Main Sequence to Red Giant
Worksheet Question: Describe the main sequence stage of a star’s life.
Answer: The main sequence represents the longest and most stable phase in a star’s life. During this period, the star burns hydrogen into helium at a steady rate, radiating light and heat into the surrounding space. Our Sun is currently in its main sequence stage. The duration of a star’s main sequence depends on its mass. More massive stars have shorter lifespans because their nuclear fusion reactions occur at a much faster rate.
Worksheet Question: What happens to a star when it runs out of hydrogen fuel in its core?
Answer: When a star exhausts its hydrogen fuel, it enters a phase of instability and begins to expand. The core collapses under the influence of gravity, leading to a rise in temperature and pressure. This increased pressure reignites fusion in a shell surrounding the core, where helium is now the fuel source. The star undergoes a dramatic expansion, becoming a red giant or a supergiant, depending on its initial mass.

Image: mavink.com
The Stellar Legacy: From White Dwarf to Supernova
Worksheet Question: What is a white dwarf, and how is it formed?
Answer: A white dwarf is the dense remnant of a star that has exhausted its nuclear fuel. It is primarily composed of carbon and oxygen, the end products of helium fusion. As a red giant sheds its outer layers, its core shrinks into a very small and incredibly dense object. A white dwarf is roughly the size of the Earth, yet it can have a mass similar to the Sun. These celestial embers slowly cool and fade over billions of years, eventually becoming black dwarfs.
Worksheet Question: Explain the process of a supernova explosion.
Answer: Supernova explosions are the spectacular and violent deaths of massive stars. When a massive star exhausts its nuclear fuel, its core collapses under its own immense gravity, leading to a catastrophic chain reaction of nuclear fusion. The core implodes, releasing a tremendous burst of energy that blows the star’s outer layers into space, creating a brilliant and expanding supernova remnant. Supernovae are the most powerful explosions in the cosmos, scattering heavy elements into the universe, seeding the formation of new stars and planetary systems.
The Cosmic Cycle: From Stellar Ashes to New Beginnings
Worksheet Question: How do elements heavier than iron form in stars?
Answer: Elements heavier than iron are formed during supernova explosions. The extreme temperatures and pressures in the supernova core allow for the fusion of iron nuclei with other particles, creating heavier elements like gold, platinum, and uranium. These elements are then ejected into the interstellar medium, eventually becoming part of new stars and planets.
Worksheet Question: What is the significance of supernovae in the universe?
Answer: Supernovae play a vital role in the evolution of the universe. These cosmic explosions are the primary sources of heavy elements, which are essential for the formation of planets and life. Supernova remnants also seed the interstellar medium with energy and material, contributing to the formation of new stars and nebulae. The cycle of stellar life and death is an ongoing process, perpetuating the creation and evolution of the universe.
Exploring the Cosmic Canvas: Resources to Deepen Your Understanding
The fascinating journey of a star’s life cycle offers a glimpse into the grand scale of the cosmos and the profound connections within the universe. To delve deeper into this captivating subject, you can explore these valuable resources:
-
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA): NASA’s website is a treasure trove of information on stars, nebulae, and supernovae. You can access stunning images, informative articles, and even interactive simulations.
-
The Hubble Space Telescope: Hubble’s breathtaking images of nebulae and supernova remnants are truly awe-inspiring. The Hubble website provides a wealth of information and resources.
-
The American Astronomical Society (AAS): The AAS website offers a wealth of information, including news articles, research papers, and educational resources related to astronomy and astrophysics.
-
Your Local Library or Planetarium: These institutions offer a wealth of resources, including books, documentaries, and stargazing events.
By exploring these resources, you can continue your journey of discovery and continue to be amazed by the celestial tapestry that unfolds before us.
Life Cycle Of A Star Worksheet Answers
Conclusion
The life cycle of a star is a majestic cosmic drama that unfolds across time and space. From the ethereal beauty of a nebula to the explosive grandeur of a supernova, each stage in a star’s life reveals the profound interplay of forces that shape the universe. The knowledge we gain from studying stars provides us with a deeper understanding of our own existence and the interconnectedness of the cosmos.
So, next time you gaze upon a star, remember that you’re witnessing a celestial ballet of creation and transformation. Reflect on the incredible journey that star has taken, and the legacy it will leave behind, forever imprinted upon the cosmic canvas. As you explore the wonders of the universe, let your curiosity guide you, and remember that the exploration of the cosmos is a voyage that knows no end.






