Imagine you’re about to embark on a thrilling journey. You meticulously plan your route, pack your bags, and ensure you have all the necessary gear. But what if, halfway through your trip, your car breaks down? Or what if you discover you’ve forgotten your passport? These issues might have been prevented with thorough preparation and quality checks. In the world of product development, quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC) play a crucial role in ensuring a smooth and successful journey. While they might seem like interchangeable terms, each plays a distinct part in guaranteeing the final product meets the highest standards.
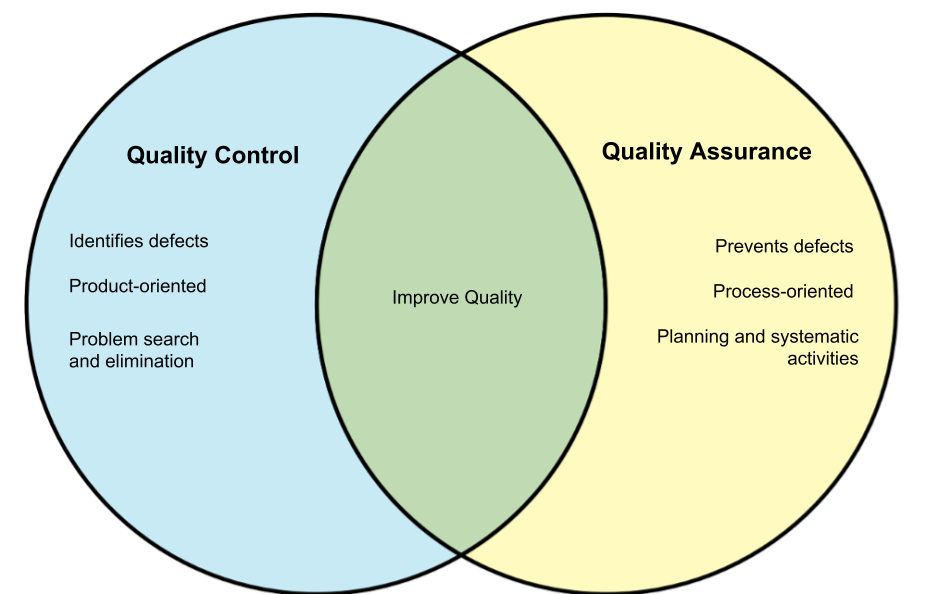
Image: diff.wiki
This article will delve into the nuances of QA and QC, explaining their methodologies, differences, and importance in helping organizations achieve their goals. From the early stages of product development to the final delivery process, both QA and QC ensure customer satisfaction and maintain competitive edge in a market driven by quality and reliability. Understanding the distinct roles of each allows businesses to optimize their quality management practices and achieve a seamless and successful product lifecycle.
What is Quality Assurance?
Quality assurance (QA) is a comprehensive approach to ensure that a product or service consistently meets predetermined quality standards. It’s a proactive, preventative measure that focuses on the process of development rather than just the final product. QA aims to minimize risks and prevent defects from occurring in the first place. Think of QA as a quality “guardian” who establishes a robust framework and sets the stage for successful product development.
Key Activities in Quality Assurance:
- Defining Quality Standards: Establishing clear and measurable quality criteria for the product or service.
- Process Audits: Regularly reviewing and monitoring development processes to identify potential weaknesses or non-compliance issues.
- Risk Management: Identifying and analyzing potential risks during development and implementing mitigation strategies.
- Training and Education: Empowering team members with necessary skills and knowledge related to quality processes.
- Documentation and Reporting: Maintaining thorough records of all QA activities and generating reports to highlight strengths, areas for improvement, and any potential issues.
What is Quality Control?
Quality control (QC) is a reactive approach that focuses on inspecting and testing finished products or services to ensure they meet predetermined quality standards. It’s like a “quality detective” who meticulously examines the product to ensure it adheres to specifications before it reaches the customer. QC is often considered a more tangible and measurable aspect of quality management.

Image: www.smlease.com
Key Activities in Quality Control:
- Inspection and Testing: Conducting rigorous inspections and tests on finished products or services to verify they meet specific criteria.
- Defect Identification and Analysis: Identifying any defects or discrepancies and analyzing their root causes.
- Corrective Actions: Implementing immediate corrective actions to address identified defects and prevent recurrence.
- Data Collection and Reporting: Tracking quality metrics, monitoring trends, and generating reports to identify areas for improvement.
Key Differences Between Quality Assurance and Quality Control
While both QA and QC strive for product excellence, their approaches and focus areas differ significantly. Understanding these differences is crucial to effectively manage quality within an organization.
Proactive vs. Reactive:
- QA: Proactive, focusing on preventing defects and ensuring compliance throughout the development process.
- QC: Reactive, focusing on detecting and fixing defects in finished products or services.
Process vs. Product:
- QA: Emphasizes process improvement and adherence to standards throughout the development lifecycle.
- QC: Primarily focused on inspecting and testing the final product or service.
Prevention vs. Detection:
- QA: Aims to prevent defects from occurring in the first place through proactive measures.
- QC: Focuses on detecting defects that have already occurred and implementing corrective actions.
Long-Term vs. Short-Term:
- QA: A continuous and ongoing process that establishes a long-term framework for quality management.
- QC: Typically a focused, short-term activity conducted to evaluate specific batches or production runs.
The Importance of Integrating QA and QC
While QA and QC have distinct roles, their integration creates a powerful synergy for achieving comprehensive quality management. By working in tandem, these two components provide a robust system for ensuring consistent product excellence.
- Enhanced Product Quality: Integrating QA and QC results in a more robust and reliable approach to achieving high-quality products.
- Reduced Costs and Risks: Preventing defects through proactive QA measures minimizes costly rework and minimizes the risk of product recalls or customer dissatisfaction.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: Delivering high-quality products that meet customer expectations leads to increased satisfaction and loyalty.
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: Streamlining quality processes through integration improves efficiency, reduces waste, and boosts overall productivity.
Real-World Examples:
The importance of QA and QC is evident in various industries, from manufacturing to software development. Here are a few real-world examples:
Manufacturing:
In the manufacturing industry, QA ensures that production processes adhere to standards and regulations, while QC verifies that finished products meet specific quality criteria. Imagine a car manufacturer. QA would be responsible for ensuring the consistency of the manufacturing process, while QC would inspect finished vehicles to ensure they meet safety and performance standards. This combination guarantees cars meet quality expectations and deliver a safe and enjoyable driving experience.
Software Development:
In software development, QA ensures that the software product meets functional requirements, usability standards, and security protocols. QC focuses on testing the software’s functionality, stability, and performance before release. For example, QA would ensure that the latest mobile app update functions properly and meets the intended user experience. QC would conduct extensive testing to validate that the app performs flawlessly on various devices and platforms. This approach leads to a seamless user experience and minimizes the risk of software bugs or performance issues.
Healthcare:
The healthcare industry utilizes rigorous QA and QC procedures to ensure the safety and efficacy of medical devices, pharmaceuticals, and diagnostic tools. QA would be involved in validating the sterile manufacturing processes for medical devices or the clinical trials of new medications. QC would inspect finished medical products to ensure they meet sterility standards, dosage accuracy, and have no defects. This stringent approach guarantees the safe and effective use of medical products, protecting patient health and well-being.
The Future of Quality Assurance and Quality Control
The future of QA and QC is driven by technological advancements and evolving customer expectations. Here are some exciting trends:
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
AI and ML are transforming QA and QC, enabling automated testing, predictive analysis, and improved defect detection. These technologies help identify patterns, anticipate potential issues, and optimize quality processes. For example, AI-powered tools can analyze large datasets to predict potential design flaws or identify manufacturing defects before they occur.
Big Data and Analytics:
Big data and analytics are enabling QA and QC teams to gain deeper insights into quality trends, customer feedback, and market dynamics. This data-driven approach allows organizations to make better-informed decisions, improve product development processes, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Digital Transformation:
Digital transformation is driving a shift towards cloud-based platforms for managing QA and QC processes. These platforms offer greater flexibility, scalability, and real-time data access, enabling better collaboration and communication among teams. This digital shift also allows organizations to leverage remote testing and remote collaboration tools, expanding their reach and maximizing efficiency.
Difference Between Quality Assurance And Quality Control Pdf
Conclusion:
In conclusion, quality assurance and quality control are essential components of any successful organization. While they have distinct roles, their integration forms a robust framework for ensuring consistent product excellence. By understanding the key differences and embracing the latest trends, organizations can optimize their quality management practices, achieve higher standards, and ultimately, deliver exceptional experiences to their customers. It’s not just about avoiding product defects, but about ensuring a seamless, reliable, and fulfilling journey for everyone involved.






