Imagine a world where your body’s vital lifeline – the blood that carries oxygen and nutrients – struggles to reach the farthest corners of your limbs. This is the reality of ineffective peripheral tissue perfusion, a hidden health concern that can leave you feeling cold, numb, and even in pain. It can affect anyone, but it’s particularly prevalent in those with underlying health conditions like diabetes, heart disease, or peripheral artery disease. But don’t despair! This article dives deep into the world of ineffective peripheral tissue perfusion, explaining its intricacies, shedding light on its effects, and offering invaluable strategies for ensuring effective care.

Image: desaininterior-01.blogspot.com
Peripheral tissue perfusion refers to the process by which blood is efficiently delivered to the extremities of your body, including your hands, feet, arms, and legs. This blood carries life-sustaining oxygen and nutrients, nourishing your tissues and removing waste products. When this process becomes impaired, it’s called ineffective peripheral tissue perfusion, a condition that can lead to a range of complications, from simple discomfort to life-threatening consequences.
Understanding the Roots of Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion
Ineffective peripheral tissue perfusion is a multifaceted issue, with a complex interplay of factors contributing to its development. Here’s a closer look at the key players involved:
1. Arterial Disease: Perhaps the most common culprit is peripheral artery disease (PAD), a condition where the arteries supplying blood to the limbs become narrowed or blocked by plaque buildup. This restricts blood flow, leading to inadequate perfusion.
2. Venous Insufficiency: The veins responsible for returning blood from the extremities to the heart can also malfunction, causing a buildup of blood in the legs and feet, known as venous insufficiency. This stagnation of blood can hinder proper tissue perfusion.
3. Diabetes: High blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can damage blood vessels over time, impairing their ability to deliver blood effectively, particularly to the lower extremities.
4. Heart Disease: Conditions like heart failure or heart valve problems can disrupt blood flow throughout the body, including the peripheral tissues.
5. Medications: Certain medications, like some chemotherapy drugs, can also have a negative impact on blood circulation, thereby impacting peripheral tissue perfusion.
The Silent Messenger: Recognizing the Signs
Recognizing the telltale signs of ineffective peripheral tissue perfusion is crucial for early intervention and optimal management. Here are some key symptoms to watch out for:
1. Coldness: One of the most common signs is experiencing coldness in your hands, feet, or legs, even in warm environments.
2. Numbness and Tingling: Reduced blood flow can lead to numbness, tingling sensations, or even burning pain in the affected extremities.
3. Discoloration: The skin on your legs or feet might appear pale or even blue due to inadequate oxygen supply.
4. Pain During Exercise: You might experience pain or discomfort in your legs when walking or exercising, a symptom commonly associated with PAD.
5. Poor Wound Healing: If wounds or ulcers on your legs are slow to heal, it could be a sign of compromised tissue perfusion.
6. Hair Loss: Reduced blood flow can lead to thinning or hair loss on your legs and feet, particularly in the toes.
7. Edema: Swelling in the legs or feet can also be a sign of impaired blood flow, especially if accompanied by other symptoms.
Navigating the Landscape of Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Care Plans: A Comprehensive Guide
Ineffective peripheral tissue perfusion demands a tailored approach to care, involving a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, and physical therapists. The creation of a comprehensive care plan is essential for effectively managing the condition and improving patient outcomes.
1. Diagnosis and Assessment: The Starting Point:
-
Thorough Medical History: Your doctor will gather information about your medical history, family history, and any current medications you’re taking.
-
Physical Exam: The doctor will assess your overall health, including checking your pulse, blood pressure, and examining your legs and feet for signs of impaired perfusion.
-
Diagnostic Testing: Imaging scans like an ankle-brachial index (ABI) test or a Doppler ultrasound can measure blood flow in your legs and identify blockages.
2. Lifestyle Modifications: A Foundation for Healing:
-
Smoking Cessation: Smoking is a major risk factor for PAD and other circulatory problems. Quitting smoking can significantly improve blood flow and overall health.
-
Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can promote better cardiovascular health and improve circulation.
-
Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, even moderate-intensity exercise, can strengthen heart function and improve blood flow to the legs.
3. Medications: Supporting Blood Flow:
-
Antiplatelet Drugs: Medications like aspirin or clopidogrel can help prevent blood clots from forming in the arteries and improve blood flow.
-
Statins: Statins are often prescribed to lower cholesterol levels, thereby reducing plaque buildup in the arteries.
-
Blood Pressure Medications: Controlling high blood pressure can reduce strain on the heart and improve blood flow.
4. Invasive Therapies: Restoring Circulation:
-
Angioplasty and Stenting: In cases of severe arterial blockages, angioplasty can be used to open up the narrowed artery, and a stent can be inserted to maintain blood flow.
-
Bypass Surgery: If angioplasty isn’t successful, bypass surgery might be necessary to create a new pathway for blood to flow around the blockage.
5. Wound Care: Preventing Infections:
-
Proper Wound Dressing: Keeping wounds clean and covered can prevent infection and promote healing.
-
Compression Therapy: Compression stockings or bandages can help improve circulation and reduce swelling in the legs.
6. Physical Therapy: Building Strength and Function:
-
Exercises for Leg Strength: Physical therapists can recommend exercises to improve leg strength and endurance, enhancing circulation and mobility.
-
Range-of-Motion Exercises: Exercises designed to increase flexibility and range of motion can help prevent stiffness and improve circulation.
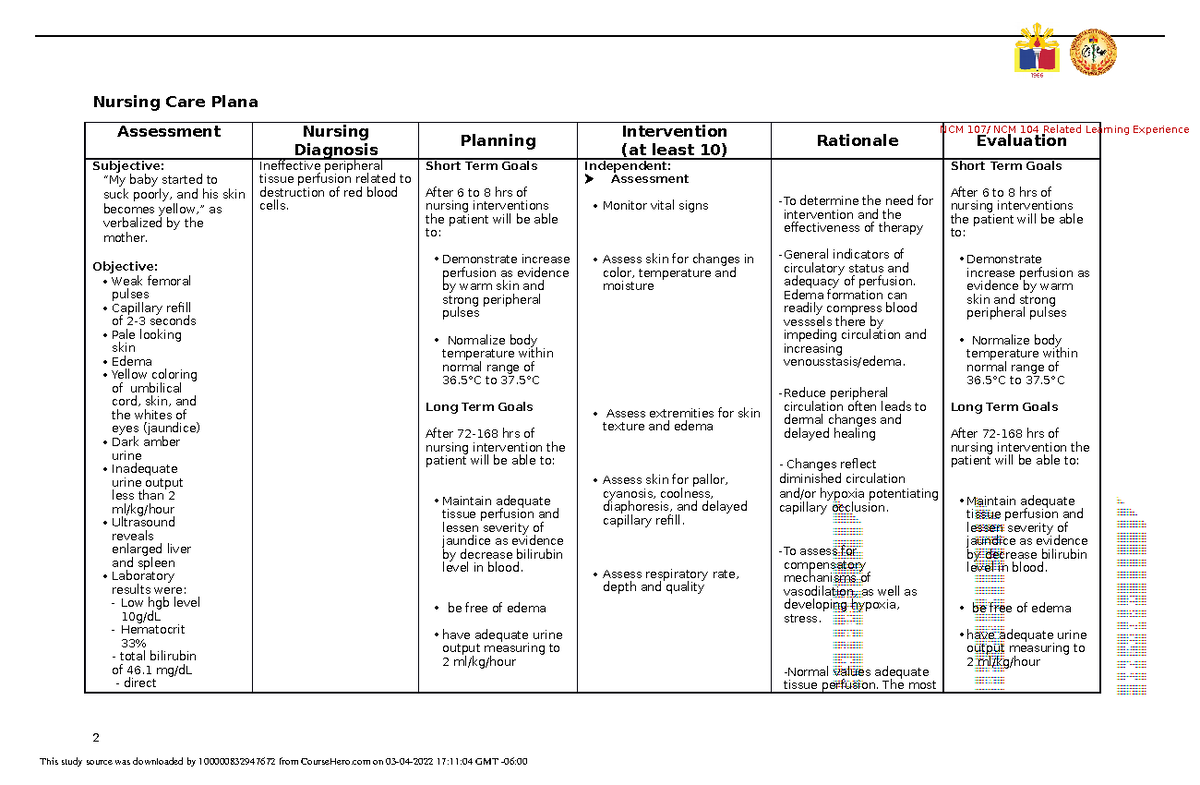
Image: www.studocu.com
Expert Insights: Empowering You to Take Action
Dr. Emily Carter, a renowned cardiologist specializing in peripheral vascular disease, advises, “Early detection and intervention are key to managing ineffective peripheral tissue perfusion. Don’t ignore any changes in your legs or feet. Consult your doctor immediately if you experience persistent coldness, numbness, tingling, or pain. Many lifestyle changes and medical therapies are available to improve circulation and prevent complications.”
Dr. Sarah Thompson, a board-certified vascular surgeon, adds, “Don’t hesitate to seek professional help, especially if you have known risk factors like diabetes, heart disease, or smoking. Timely diagnosis and treatment can significantly reduce your risk of amputation and improve your quality of life.”
Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Care Plan
https://youtube.com/watch?v=IiwNCD6R8ZQ
A Call to Action: Taking Charge of Your Health
Ineffective peripheral tissue perfusion, while often silent, can have a profound impact on your well-being. Armed with knowledge and proactive action, you can empower yourself to live a healthier life.
-
Consult your doctor: Schedule a regular check-up with your healthcare provider to discuss your risk factors and undergo necessary screenings.
-
Embrace a healthy lifestyle: Prioritize good diet, exercise, and smoking cessation to promote healthy blood flow and overall cardiovascular health.
-
Be your own advocate: Listen to your body and speak up about any concerns you may have. Early detection and intervention are crucial in managing ineffective peripheral tissue perfusion.
By understanding this condition and taking charge of your health, you can pave the way for a brighter, healthier future.






