The moment a mother holds her newborn for the first time is a magical experience, often painted with joy and relief. However, this happy occasion can sometimes be shadowed by anxieties, especially regarding postpartum bleeding. As a nurse, I’ve seen firsthand the emotional roller coaster women navigate during this period. From the overwhelming excitement of new parenthood to the apprehension of potential complications, the postpartum journey is a complex one. One of the most prevalent and serious concerns is excessive bleeding after childbirth, which can not only affect a mother’s physical health but also her emotional well-being. Understanding the risks and implementing a comprehensive nursing care plan is crucial for ensuring a safe and healthy transition for new mothers.
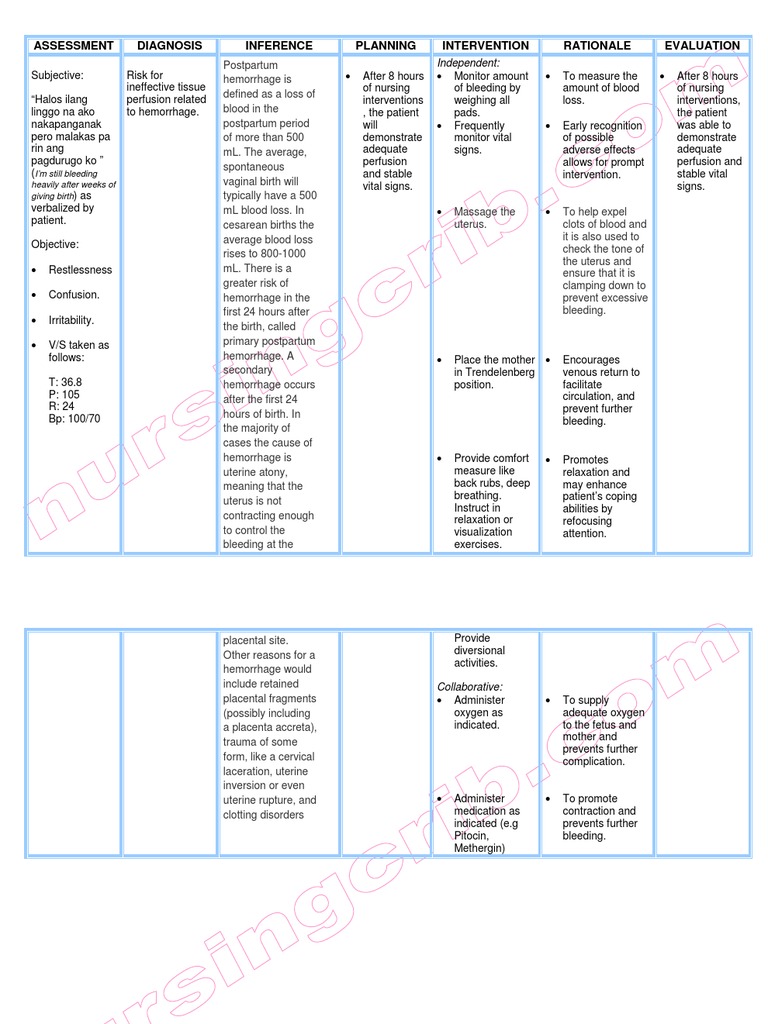
Image: www.scribd.com
In this article, we’ll delve into the world of postpartum bleeding, exploring its causes, risk factors, and most importantly, the nursing interventions aimed at preventing and managing this potential complication. We’ll uncover the significance of a well-structured care plan, emphasizing the role of continuous monitoring, proactive interventions, and skilled nursing care in ensuring a positive postpartum experience for every mother.
Understanding Postpartum Bleeding
Defining Postpartum Hemorrhage
Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH), a leading cause of maternal mortality worldwide, is defined as excessive blood loss after childbirth. The definition varies based on the timing and volume of blood loss. Generally, it’s considered to be:
- Early PPH: Blood loss exceeding 500ml within the first 24 hours after delivery
- Late PPH: Blood loss exceeding 500 ml after 24 hours and up to 12 weeks postpartum
The severity of PPH can range from mild, requiring minimal interventions, to life-threatening, necessitating immediate emergency care. Recognizing the signs of excessive bleeding and acting swiftly is critical in preventing serious complications.
Causes and Risk Factors
The causes of postpartum bleeding are multifaceted, encompassing both physiological and anatomical factors. Some of the most common causes include:
- Uterine Atony: Failure of the uterus to contract adequately after delivery, leading to excessive bleeding from the placental site.
- Retained Placenta: A part or the whole placenta remains in the uterus after delivery.
- Lacerations: Tears in the cervix, vagina, or perineum during delivery.
- Uterine Inversion: The uterus turns inside out, usually during delivery of the placenta.
- Blood Clotting Disorders: Inherited or acquired conditions affecting the blood’s ability to clot, leading to increased bleeding.
Certain factors can increase a woman’s risk of experiencing postpartum bleeding. These include:
- Previous PPH: Women who have experienced PPH in previous pregnancies have a higher risk of experiencing it again.
- Multiple Pregnancies: Women who have had multiple pregnancies are more likely to experience uterine atony.
- Premature Birth: Premature births often result in a weaker uterus and increased risk of bleeding.
- Large Baby: Delivering a large baby can put stress on the uterus, increasing the risk of atony.
- Placenta Previa: When the placenta attaches low in the uterus, covering part or all of the cervical opening.
- Obesity: Women with obesity are at a higher risk of PPH due to increased blood volume and altered clotting factors.
- Medical Conditions: Certain underlying medical conditions like diabetes, anemia, or hypertension, can increase the risk of postpartum bleeding.
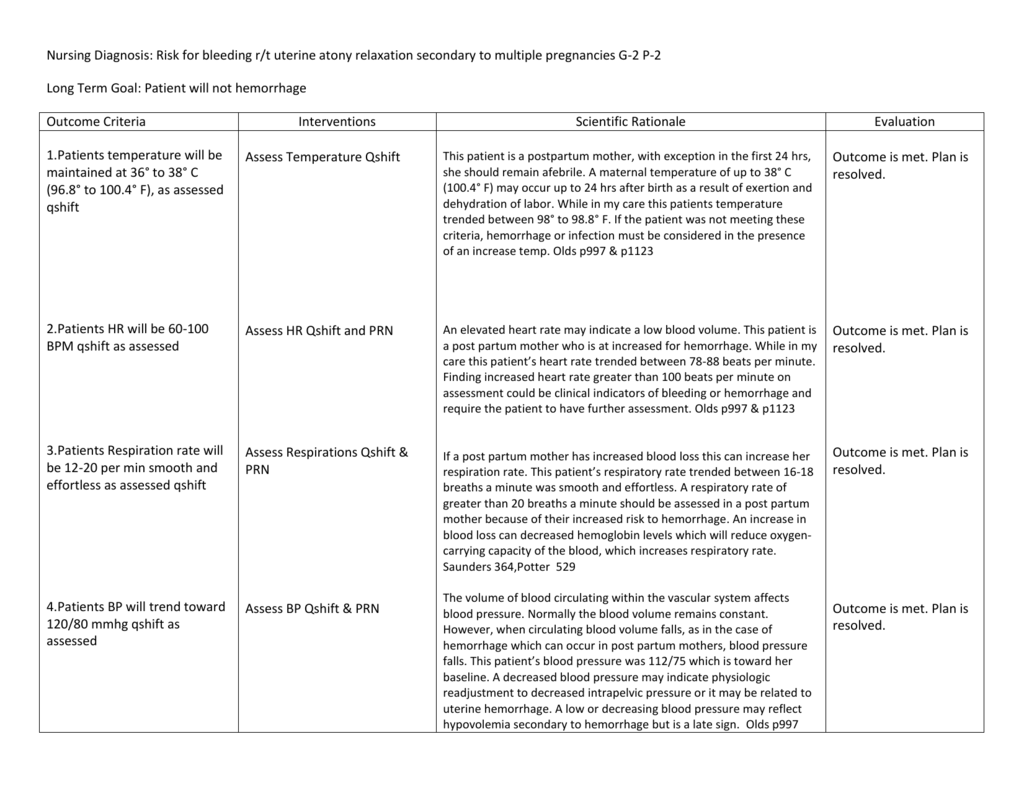
Image: slidesharetrick.blogspot.com
The Importance of a Nursing Care Plan for Risk of Bleeding
A comprehensive nursing care plan plays a vital role in preventing and managing postpartum bleeding. By integrating continuous assessment, timely intervention, and education for the mother and family, nurses play a crucial role in safeguarding a mother’s health and facilitating a smooth postpartum recovery.
Key Components of a Nursing Care Plan
A well-structured nursing care plan for the risk of bleeding postpartum encompasses several essential components, including:
- Assessment: Frequent assessments are critical in identifying early signs of PPH. This includes monitoring vital signs, assessing the uterus for firmness and position, and evaluating the volume and character of lochia (vaginal discharge after childbirth).
- Intervention: The choice of interventions depends on the cause and severity of bleeding. Some common interventions include:
- Uterine Massage: Gentle massage of the uterus can help it contract and reduce bleeding.
- Medications: Drugs such as oxytocin and methylergonovine are used to stimulate uterine contractions.
- Fluid Replacement: Intravenous fluids are given to maintain blood volume and prevent shock.
- Blood Transfusions: Blood transfusions may be necessary in cases of significant blood loss.
- Surgical Interventions: In severe cases, surgery may be required to control bleeding, including dilation and curettage, hysterectomy, or ligation of the uterine arteries.
- Education: Instructing the mother and family about signs and symptoms of postpartum bleeding, warning signs, and self-care measures is crucial for effective management and early intervention.
- Emotional Support: Providing emotional support to the new mother and her partner during this stressful period is essential for their well-being.
Promoting a Safe and Healthy Postpartum Recovery
The nursing care plan for a woman at risk for postpartum bleeding focuses on prevention and early detection. By implementing a proactive approach, nurses can help minimize the risk of complications and promote a safe and healthy postpartum recovery for the new mother.
Tips and Expert Advice
Based on my experience as a nurse, here are some essential tips and advice for new mothers and their families regarding postpartum bleeding:
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids helps your body recover and minimizes the risk of dehydration, which can worsen bleeding.
- Rest as Much as Possible: Your body needs adequate rest to heal and recover from childbirth.
- Seek Medical Attention Immediately: If you experience excessive bleeding, soaking more than one pad per hour, or any other alarming signs, contact your doctor or seek emergency medical attention right away.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Focus on nutrient-rich foods that aid in recovery and promote blood clotting.
- Learn About Your Risk Factors: Understanding your individual risk factors for postpartum bleeding can empower you to take proactive steps to minimize the risk.
FAQ
- Q: How can I prevent postpartum bleeding?
- A: While not all postpartum bleeding can be prevented, you can minimize the risk by maintaining a healthy weight, getting prenatal care, and being aware of your risk factors.
- Q: What are the signs and symptoms of postpartum bleeding?
- A: Signs include excessive bleeding, soaking through more than one pad per hour, passing large clots, experiencing pain and pressure in your abdomen, feeling weak or dizzy, and having a rapid heartbeat.
- Q: Is postpartum bleeding always a serious concern?
- A: Not always, but it’s essential to seek medical attention immediately to rule out any potential complications.
- Q: What are the long-term effects of postpartum bleeding?
- A: If left untreated, postpartum bleeding can lead to anemia, infection, and in some cases, death. However, with prompt management, most women make a full recovery.
- Q: How long does postpartum bleeding usually last?
- A: Postpartum bleeding typically lasts for 4-6 weeks. However, it can vary depending on individual factors.
Nursing Care Plan Risk For Bleeding Postpartum
Conclusion
Postpartum bleeding is a common complication that can have a significant impact on a mother’s health and well-being. A comprehensive nursing care plan emphasizes the importance of early detection, timely intervention, and continuous monitoring to minimize the risk of complications and promote a safe and healthy postpartum recovery. As nurses, we play a crucial role in providing education and emotional support to new mothers and their families to ensure a positive postpartum experience for every mother.
Are you interested in learning more about postpartum bleeding or other related topics? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below. We’re here to help you navigate the postpartum journey with confidence and ease.






