Imagine a new mother, exhilarated by the arrival of her baby, yet haunted by the fear of excessive bleeding. Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH), a terrifying complication that can occur after childbirth, is a reality for many women, leaving them vulnerable and their families worried. Understanding the risks and the comprehensive care plan in place to prevent and manage PPH is crucial for a safe and fulfilling journey into motherhood.

Image: nurseslabs.com
This article delves into the world of postpartum hemorrhage, outlining the risk factors, the meticulous care plan designed to mitigate these risks, and the importance of early intervention for optimal maternal health. Join us as we shed light on this critical topic ensuring every woman receives the best possible care during a time of profound change and joy.
Understanding Postpartum Hemorrhage
Defining Postpartum Hemorrhage
Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) is defined as the loss of more than 500 ml of blood after vaginal delivery or more than 1000 ml after a cesarean section. While these numbers may seem abstract, it is important to understand that even seemingly small amounts of blood loss can significantly impact a woman’s health.
Types of Postpartum Hemorrhage
Postpartum hemorrhage occurs in two distinct forms: early and late.
- Early Postpartum Hemorrhage: Occurs within the first 24 hours after delivery. This is the most common type of PPH, accounting for the majority of cases.
- Late Postpartum Hemorrhage: Occurs between 24 hours and 12 weeks after delivery. While less frequent, late PPH can be equally dangerous.
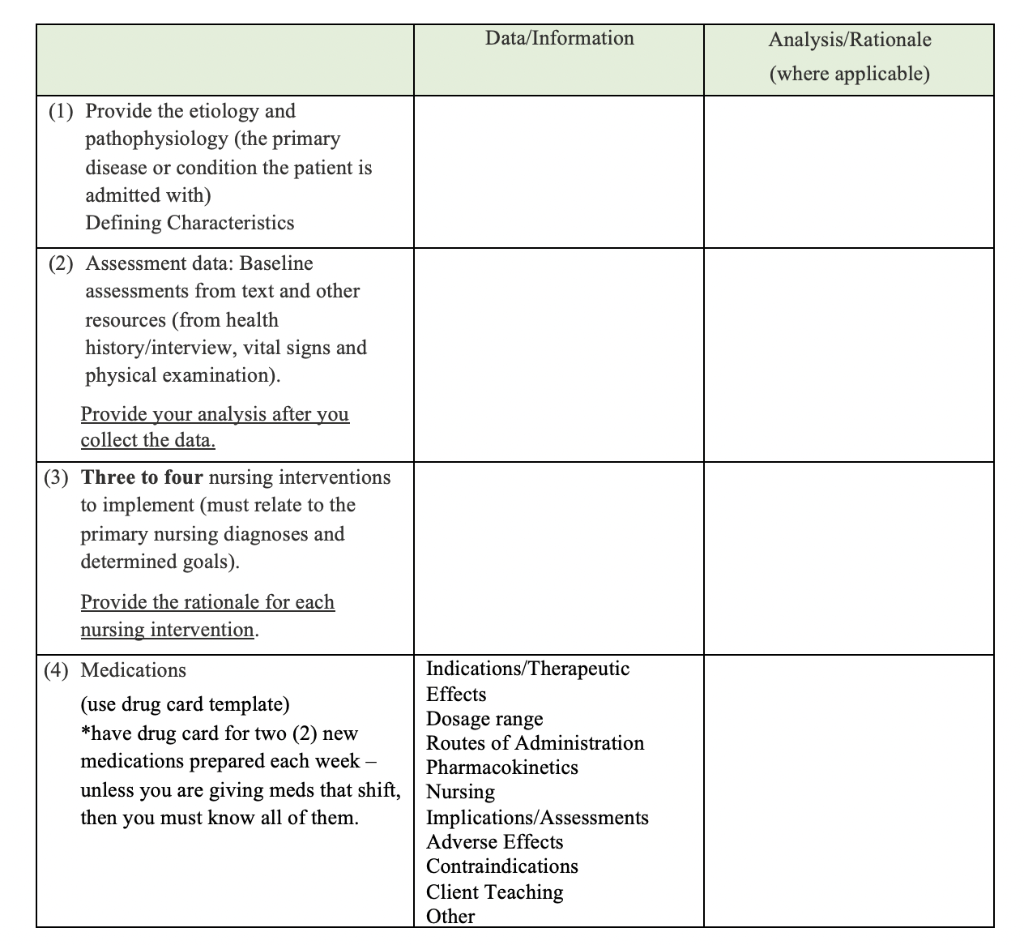
Image: www.vrogue.co
Risk Factors for Postpartum Hemorrhage
Understanding the risk factors associated with PPH is essential for proactive care. These factors can be categorized into several areas:
Maternal Factors
- Previous history of PPH: Women who have experienced PPH in a previous pregnancy are at significantly higher risk of experiencing it again.
- Multiple pregnancies: Women carrying multiple fetuses (twins, triplets, etc.) are more susceptible to PPH due to the increased uterine stretching and blood flow.
- Large baby size: Delivering a baby with a higher birth weight increases the risk of PPH as it puts extra strain on the uterus.
- Premature birth: Premature infants require more medical intervention during labor and delivery, increasing the potential for bleeding complications.
- Medical conditions: Existing medical conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, or blood clotting disorders can increase the risk of PPH.
- Uterine fibroids: These non-cancerous growths in the uterus can interfere with uterine contractions, making it harder to control bleeding after delivery.
- Placental abnormalities: Conditions like placenta previa, where the placenta is positioned low in the uterus, or placenta accreta, where the placenta grows too deeply into the uterine wall, can increase the risk of PPH.
Labor and Delivery Factors
- Labor induction: Medications used for labor induction can sometimes cause uterine overstimulation, potentially leading to PPH.
- C-section: Cesarean deliveries carry a higher risk of PPH compared to vaginal deliveries due to the surgical incision into the uterus.
- Prolonged labor: Extended labor can exhaust the uterus, reducing its ability to contract and control bleeding.
- Assisted delivery: Use of forceps or vacuum extraction during delivery can increase the risk of uterine trauma and subsequent bleeding.
The Postpartum Hemorrhage Care Plan
Recognizing the significant risk of PPH, healthcare providers have developed a comprehensive care plan aimed at preventing and treating this potentially life-threatening condition. This care plan, implemented throughout the pregnancy and postpartum period, focuses on:
Prevention
The cornerstone of PPH care lies in its prevention. Early identification and management of risk factors are key.
- Pre-pregnancy counseling: This includes discussing medical history, previous pregnancies, and any existing health conditions to identify potential risks and implement appropriate preventive measures.
- Early identification of risk factors: Monitoring women throughout pregnancy for any signs or symptoms of complications that could lead to PPH is crucial.
- Careful management of labor and delivery: This includes using appropriate medications, minimizing interventions, and ensuring timely delivery when necessary.
- Close monitoring after delivery: Continuous observation of vital signs, uterine tone, and blood loss is essential in the immediate postpartum period.
Treatment
Should PPH occur, prompt and effective treatment is paramount. The care plan aims to control bleeding, stabilize the mother’s condition, and address any underlying causes.
- Uterine massage: Gentle massage of the uterus helps stimulate contractions, which can help control bleeding.
- Medications: Medications like oxytocin and misoprostol are often used to enhance uterine contractions and reduce bleeding.
- Blood transfusions: If significant blood loss occurs, blood transfusions are used to restore blood volume and maintain the mother’s vital signs.
- Surgical interventions: In some cases, surgical interventions like uterine artery ligation or hysterectomy may be necessary to control bleeding.
Early Intervention: The Key to Successful Management
The most important aspect of managing PPH is recognizing its early signs and symptoms. Prompt intervention is critical for successful treatment and ensuring a positive outcome for the mother. Common signs include:
- Heavy vaginal bleeding: The bleeding may be bright red, dark red, or even with clots.
- Increased heart rate: The body tries to compensate for blood loss by increasing the heart rate.
- Low blood pressure: As the blood volume drops, the blood pressure decreases.
- Weakness or dizziness: The lack of blood flow can cause weakness and dizziness.
- Pale skin: As the blood volume decreases, the skin may appear pale.
- Rapid breathing: The body tries to compensate for the decreased blood flow by breathing rapidly.
If any of these signs occur, it is vital to seek immediate medical attention. Do not hesitate to alert the medical professionals in your care.
The Role of a Holistic Approach
Managing PPH effectively requires a collaborative approach that extends beyond just the medical aspects. Support systems play a crucial role in ensuring a mother’s recovery and well-being.
- Emotional support: The experience of PPH can be deeply distressing for both the mother and her family. Emotional support from loved ones, healthcare professionals, and support groups is essential.
- Education and awareness: Providing comprehensive information about PPH to expectant mothers and their families empowers them with knowledge, increasing their awareness of potential risks and strategies for early intervention.
- Postpartum follow-up care: Regular follow-up care after delivery helps monitor the mother’s recovery, ensure any underlying causes of PPH are addressed, and offer psychological support if needed.
Looking Ahead: Innovations and Future Directions
The medical community continues to advance research and innovation in the field of PPH care, pushing the boundaries of prevention and management. Exciting developments include:
- Novel medications: Research is ongoing to develop more effective and targeted medications to help control bleeding after childbirth.
- Non-invasive techniques: New non-invasive techniques are being explored to estimate blood loss, potentially leading to earlier detection and intervention for PPH.
- Personalized care plans: Tailoring PPH care plans to individual risk factors and patient needs can optimize prevention and treatment strategies.
Risk For Postpartum Hemorrhage Care Plan
Conclusion: Empowering Mothers, Ensuring Safety
The risk for postpartum hemorrhage care plan is a testament to the dedication of medical professionals to ensure the safety and well-being of mothers during this transformative time in their lives. Understanding PPH, its risk factors, and the care plan in place helps empower women and their families, enabling them to navigate this potential complication with confidence and knowledge. Remember, proactive prevention, early intervention, and a holistic approach all contribute to a positive and healthy outcome for every mother.






