Have you ever wondered what happens inside your brain when you learn something new, feel an emotion, or make a decision? It’s all thanks to the amazing and complex world of neurons! These specialized cells are the building blocks of our nervous system, responsible for transmitting information throughout our bodies. From simple reflexes to intricate thoughts, every action, thought, and feeling is a result of neuron communication. Understanding neuron anatomy and physiology unlocks a deeper understanding of how our brains work, and Review Sheet 13 provides a fantastic starting point for this journey.

Image: anatomyworksheets.com
This guide aims to provide a clear and concise breakdown of the key concepts covered in Review Sheet 13, offering a comprehensive understanding of neuron anatomy and physiology. We’ll explore the structure of a neuron, how electrical and chemical signals are transmitted, and the different types of neurons that make up our nervous system. So, whether you’re a student preparing for an upcoming exam or simply curious about the intricacies of the human brain, buckle up and get ready to dive deep into the fascinating world of neurons!
Unraveling the Secrets of the Neuron: A Deeper Dive
Neurons are the fundamental units of our nervous system, responsible for processing and transmitting information. They are specialized cells with a unique structure that allows them to communicate efficiently with each other. Understanding this structure is crucial to grasping how neurons function.
The neuron’s structure can be broken down into three main parts: the cell body or soma, dendrites, and axon. The cell body is the neuron’s control center, containing the nucleus and other organelles necessary for the cell’s survival and function. Dendrites, branching structures extending from the cell body, act like antennas, receiving signals from other neurons. The axon, a long, slender projection, acts as the neuron’s output, transmitting signals to other neurons, muscles, or glands.
The Neural Symphony: Electrical and Chemical Communication
Imagine a complex symphony where instruments communicate through a coordinated interplay of sounds. Similarly, neurons communicate through a combination of electrical and chemical signals. The electrical signal, known as an action potential, travels along the axon. When this signal reaches the end of the axon, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters, chemical messengers that cross the synapse, a tiny gap between neurons, and stimulate the next neuron.
This process of communication is essential for all aspects of our nervous system function, from sensory perception and motor control to learning and memory. Understanding how signals are generated, transmitted, and received within neurons is essential for understanding the complexity of brain function.
Exploring the Neuron’s Diverse Roles: Types and Functions
The nervous system is incredibly diverse, with different types of neurons responsible for specific functions. These include:
- Sensory neurons: These neurons carry information from our senses (sight, smell, touch, taste, and hearing) to the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord).
- Motor neurons: These neurons transmit signals from the central nervous system to muscles and glands, controlling movement and bodily functions.
- Interneurons: These neurons act as intermediaries, connecting other neurons within the brain and spinal cord. They play a crucial role in complex processes like learning, memory, and decision-making.
Understanding the different types of neurons and their specialized roles is crucial for understanding the intricate workings of the nervous system. Review Sheet 13 provides a foundation for further exploration into the diverse world of neurons.
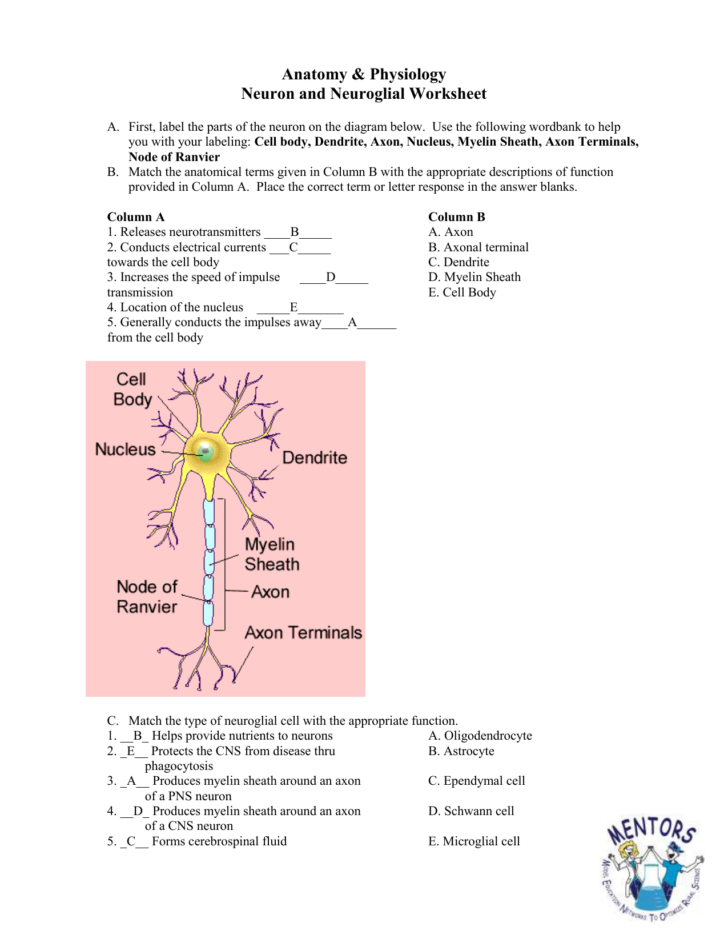
Image: www.vrogue.co
Unlocking Neural Secrets: The Latest Developments and Trends
The field of neuroscience is constantly evolving. New technologies allow us to study the brain with unprecedented detail, shedding light on the intricate mechanisms underlying neuron function. Research focuses on areas like:
- Neurogenesis: The process of generating new neurons in the brain, offering new hope for treating neurological disorders.
- Synaptic plasticity: The ability of synapses to change strength over time, a key mechanism for learning and memory.
- Neuromodulation: Using techniques like brain stimulation to modulate brain activity and treat disorders like Parkinson’s disease and depression.
These advancements hold immense promise for understanding and treating neurological diseases, improving our quality of life, and enhancing our understanding of the human brain.
Expert Tips for Aceing Review Sheet 13
Mastering the concepts in Review Sheet 13 involves active learning and a structured approach. Here are some expert tips to help you succeed:
- Active recall: Instead of simply rereading the material, test yourself regularly by recalling concepts. Use flashcards, quizzes, or even talking to yourself to reinforce your understanding.
- Visualize complex concepts: Draw diagrams or use online resources to visualize the structure and function of neurons. Creating visual representations can help solidify your understanding.
- Connect concepts: Don’t view each topic in isolation. Look for connections between different aspects of neuron anatomy and physiology. This will help you see the bigger picture and understand how all the parts work together.
- Practice, practice, practice: The more you engage with the material, the better you will understand it. Work through practice problems, study groups, and ask your instructor questions. Consistent practice is key!
Remember that understanding neuron anatomy and physiology is a journey. Be patient with yourself and embrace the process of active learning. With consistent effort and these expert tips, you’ll be well on your way to understanding the intricacies of our nervous system.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are the different parts of a neuron?
A: A neuron is composed of three main parts: the cell body (soma), dendrites, and axon.
Q: How do neurons transmit signals?
A: Neurons communicate through a combination of electrical and chemical signals. The electrical signal, known as an action potential, travels along the axon. When this signal reaches the end of the axon, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters, chemical messengers that cross the synapse and stimulate the next neuron.
Q: What are the different types of neurons?
A: There are three main types of neurons: sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. Each type has a unique function in the nervous system.
Q: What are some recent advancements in neuroscience?
A: Recent advancements in neuroscience include research into neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity, and neuromodulation. These advancements offer hope for treating neurological disorders and improving our understanding of the brain.
Review Sheet 13 Neuron Anatomy And Physiology
Conclusion
Review Sheet 13 provides a crucial foundation for understanding neuron anatomy and physiology. By diligently studying the structure, function, and communication of neurons, you gain a deeper appreciation for the remarkable complexity of our nervous system. This knowledge empowers you to better understand how our brains learn, think, feel, and move.
Are you interested in learning more about the fascinating world of neurons? Let’s continue exploring the wonders of the brain together!






