Imagine a patient, Ms. Jones, 65 years old, admitted to the hospital with a burning sensation during urination and frequent trips to the bathroom. Her urine is cloudy, and she feels a general discomfort in her lower abdomen. This is a common scenario that nurses encounter daily, a patient suffering from a urinary tract infection (UTI). As nurses, we play a crucial role in providing comprehensive care to manage and alleviate the symptoms associated with UTIs, ensuring that patients receive the best possible treatment and achieve a swift recovery.
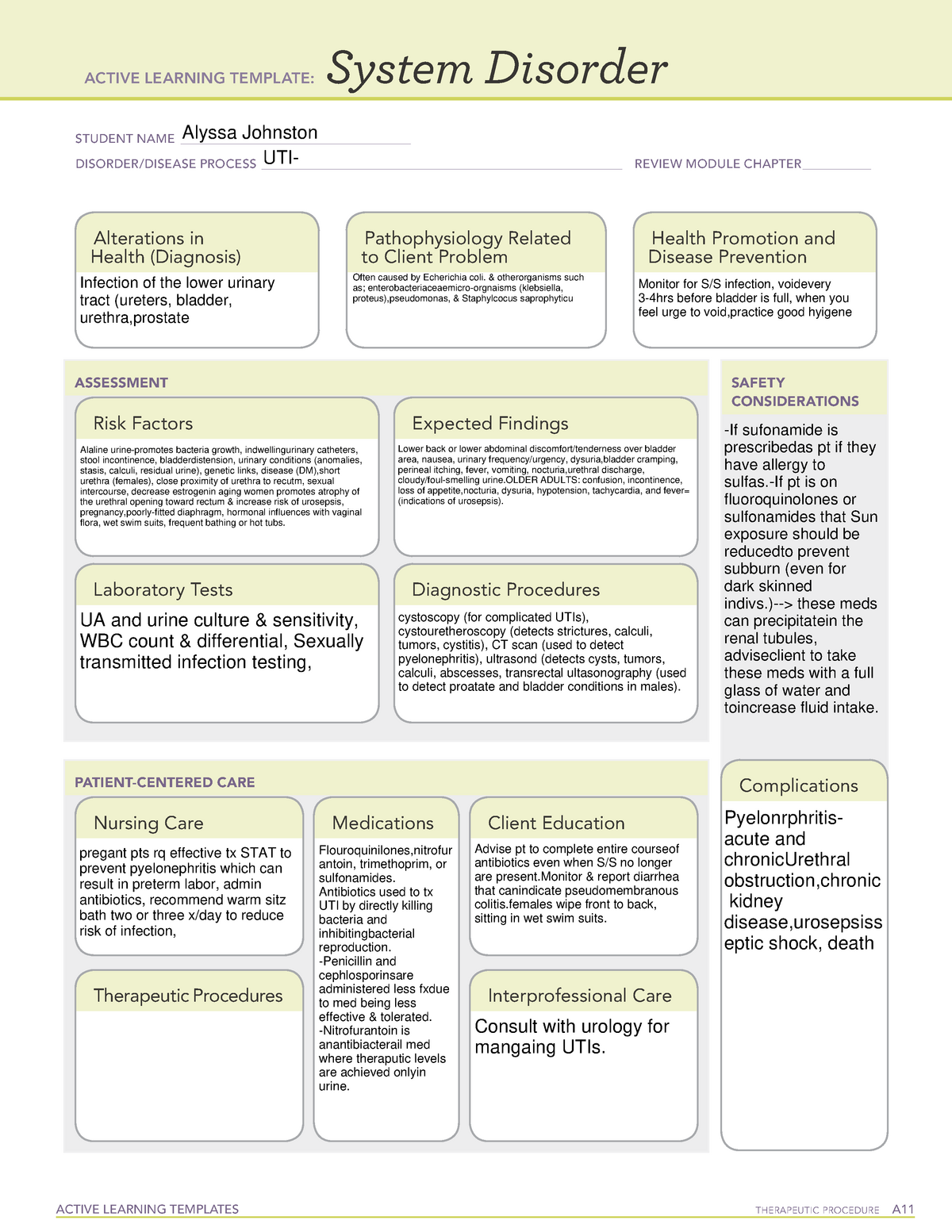
Image: template.mapadapalavra.ba.gov.br
Navigating the complexities of UTI care involves a meticulous approach that encompasses a deep understanding of the condition, its causes, and potential complications. This article will delve into the intricacies of UTI care, exploring the nursing care plan that guides our interventions and helps patients regain their health and well-being.
Understanding Urinary Tract Infections
A UTI is an infection that occurs anywhere along the urinary tract, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The most common type of UTI affects the bladder, known as cystitis. UTIs are caused by bacteria, typically Escherichia coli (E. coli), entering the urinary tract and multiplying. The bacteria can travel up the urethra and infect the bladder, and if left untreated, they may ascend to the kidneys, leading to a more serious infection called pyelonephritis.
A variety of factors can increase the risk of developing a UTI, including:
- Female anatomy: Women are more susceptible to UTIs due to their shorter urethra, which allows bacteria easier access to the bladder.
- Age: Older adults are at increased risk due to changes in the immune system and the urinary tract.
- Catheterization: Indwelling catheters can provide a pathway for bacteria to enter the bladder.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes may have higher levels of glucose in their urine, which can attract bacteria.
- Kidney stones: Stones can obstruct the flow of urine, creating a favorable environment for bacterial growth.
- Weakened immune system: Individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy, are more susceptible to UTIs.
Nursing Care Plan: A Comprehensive Approach
The nursing care plan for a patient with a UTI is a detailed roadmap that outlines the interventions required to manage the infection, alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and promote patient recovery. This plan is tailored to each individual patient, considering their specific needs, risk factors, and medical history. The key elements of a UTI nursing care plan include:
Assessment: Gathering Information About the Patient
The nursing assessment is the first step in developing a UTI care plan. We gather comprehensive information about the patient’s condition, including:
- Symptoms: Pain or burning during urination, frequent urination, urgency to urinate, blood in the urine, cloudy urine, lower abdominal pain, fever, chills, nausea, and vomiting.
- Medical history: Previous UTIs, diabetes, kidney stones, or other conditions that may increase UTI risk.
- Social history: Sexual activity, hygiene practices, and hydration levels.
- Medication history: Any medications being taken, including antibiotics.

Image: www.coursehero.com
Diagnosis: Identifying the Underlying Cause
The nurse collaborates with the physician to diagnose the UTI and determine the causative organism. The diagnosis often relies on a urine culture and sensitivity test, which helps identify the specific bacteria and determine the most effective antibiotic treatment.
Planning: Setting Goals and Choosing Interventions
After gathering information and establishing the diagnosis, we develop a comprehensive care plan. The primary goal of the care plan is to reduce the UTI symptoms and prevent complications.
Implementation: Putting the Care Plan into Action
The nursing care plan for a UTI involves the following interventions:
- Administering antibiotics: Antibiotics are the mainstay of UTI treatment, aimed at eliminating the infection. We ensure patients understand the importance of completing the full course of antibiotics, even if they feel better before completing the prescription.
- Pain management: Administering analgesics, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, to alleviate pain and discomfort. Heat therapy, such as applying a heating pad to the lower abdomen, can also be helpful.
- Fluid management: Encouraging increased fluid intake, especially water, to help flush bacteria from the urinary tract and promote urine production. We also monitor for signs of dehydration, such as dry mouth, thirst, and decreased urine output.
- Hygiene promotion: Educating patients on proper hygiene practices, including wiping front to back after urination and bowel movements, and ensuring that they empty their bladders regularly to prevent urine retention. This is especially important for women who may be prone to UTIs.
- Urinary catheter care: If the patient is using an indwelling urinary catheter, we emphasize proper hygiene and care of the catheter to prevent infection.
- Monitoring for complications: Keeping a watchful eye for signs of complications, such as fever, chills, back pain, nausea, vomiting, or changes in urine output, and reporting any concerns to the physician immediately.
Evaluation: Assessing the Effectiveness of Interventions
Throughout the care plan, nurses continuously monitor the patient’s progress, reviewing their symptoms and evaluating the effectiveness of interventions. We assess the response to antibiotic therapy, the patient’s pain levels, and their ability to manage fluid intake, making adjustments to the care plan as needed.
Latest Trends & Developments in UTI Care
The field of UTI care is constantly evolving, with ongoing research and advancements in diagnostics, treatments, and prevention strategies. Some key trends include:
- Personalized medicine: With the development of advanced genetic testing, researchers are exploring the possibility of personalized UTI treatments tailored to individual patients’ genetic profiles.
- Novel antibiotics: Researchers are continuously developing new antibiotics to combat emerging drug-resistant bacteria, improving the efficacy of UTI treatment.
- Non-antibiotic therapies: Alternative therapies, such as cranberry supplements and probiotics, are being investigated as potential preventative measures for UTIs.
- Telehealth: Telehealth platforms are increasingly used for UTI diagnosis and management, allowing patients to receive care remotely, especially in rural areas or for individuals who have difficulty accessing healthcare.
Tips and Expert Advice
While medications and medical interventions are crucial in treating UTIs, several lifestyle modifications and preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of recurrence. Here are some expert-backed tips for staying healthy and preventing UTIs:
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids, especially water, helps flush bacteria out of the urinary tract.
- Urinate frequently: Emptying the bladder regularly prevents urine retention, which can provide a breeding ground for bacteria.
- Practice good hygiene: Wiping front to back after urination and bowel movements can prevent bacteria from entering the urethra.
- Avoid irritants: Certain substances, like bubble baths, perfumed soaps, and feminine hygiene products, can irritate the urethra and increase UTI risk. Choose gentle, unscented products.
- Consider cranberry supplements: While more research is needed, some studies suggest that cranberry supplements may help prevent UTIs.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity can increase UTI risk, so maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise is important for overall health.
FAQ: Your Urinary Tract Infection Questions Answered
Here are some frequently asked questions about UTIs:
How do I know if I have a UTI?
Common UTI symptoms include burning or pain during urination, frequent urination, urgency to urinate, blood in the urine, cloudy urine, lower abdominal pain, fever, chills, nausea, and vomiting. If you experience any of these symptoms, consult with your healthcare provider.
What can I do to prevent UTIs?
Several lifestyle changes can help prevent UTIs, including staying hydrated, urinating frequently, practicing good hygiene, avoiding irritants, considering cranberry supplements, and maintaining a healthy weight.
What are the risks of untreated UTIs?
If left untreated, UTIs can spread to the kidneys, leading to pyelonephritis, a more serious infection that can cause fever, chills, back pain, nausea, vomiting, and even sepsis. Untreated UTIs can also lead to kidney damage and scarring in some cases.
When should I see a doctor?
You should seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of a UTI, especially if the symptoms are severe or persistent. UTIs require prompt treatment to prevent complications.
Can men get UTIs?
Yes, men can get UTIs, though they are less common than in women. UTIs in men can be caused by a variety of factors, including enlarged prostate, urinary stones, and catheterization.
Nursing Care Plan For Urinary Tract Infection
Conclusion
UTIs are a common and often uncomfortable condition that can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life. As nurses, we play a vital role in providing comprehensive care for patients with UTIs, ensuring that they receive prompt diagnosis, effective treatment, and appropriate education to minimize the risk of complications and promote recovery. By understanding the complexities of UTIs, implementing a well-structured care plan, and staying informed about the latest trends and developments in UTI care, nurses can continue to enhance the lives of patients facing this common condition.
Are you interested in learning more about UTI management and prevention? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below!






