Have you ever thought about the number line? It stretches infinitely in both directions, and yet within this expanse, there’s a fascinating realm of numbers that might not be instantly obvious – the realm of rational numbers. While integers, the whole numbers, feel straightforward and grounded, rational numbers encompass a vast array of fractions, decimals, and even percentages. And among these numbers exist a whole category that isn’t quite an integer, but still very much a part of the rational world.
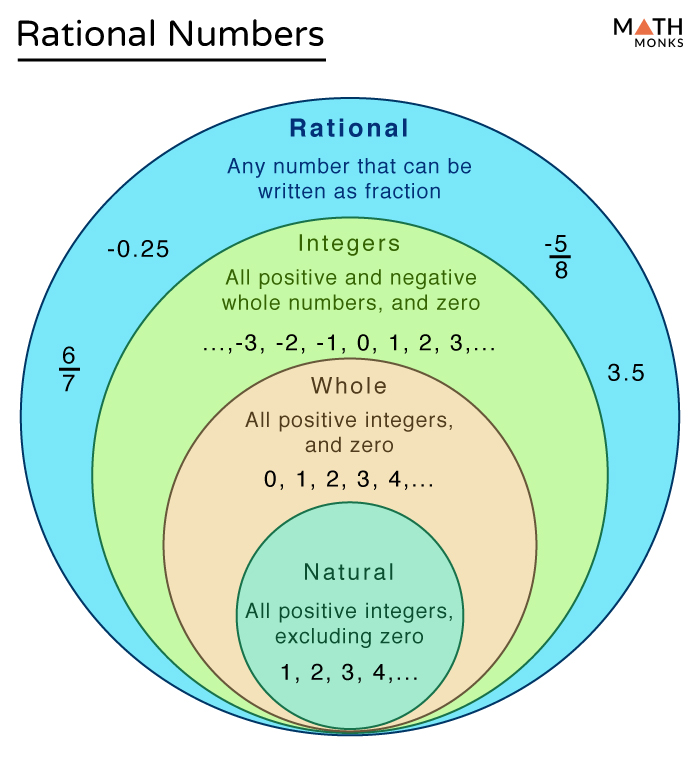
Image: ar.inspiredpencil.com
Think about a simple slice of pizza. If you divide it into four equal pieces, each slice represents a quarter of the whole pizza. Each slice is not a whole pizza, but instead, a fraction, a representation of a part of the whole. These fractions, like 1/4, 1/2, or 3/4, are examples of rational numbers that are not integers. They are numbers that can be expressed as a ratio of two integers, but they fall between the whole numbers on the number line.
Understanding the Difference Between Rational Numbers and Integers
To truly grasp the concept of rational numbers that aren’t integers, we need to understand the definitions of both. In simple terms, an integer is any whole number, including positive, negative, and zero. They represent a complete unit, like 1 apple, 3 cars, or -5 degrees Celsius. Integers are represented on the number line as single points without any fractions or decimals in between.
Rational numbers, on the other hand, are a larger category. They include all numbers that can be expressed as a fraction, where the numerator and denominator are both integers and the denominator is not zero. This means integers are a subset of rational numbers, as every integer can be expressed as a fraction with a denominator of 1 (e.g., 5 = 5/1). Yet, there are countless rational numbers that are not integers – these are the numbers that exist between two consecutive integers on the number line.
Types of Rational Numbers that are not Integers
There are two main categories of rational numbers that are not integers:
- Fractions: These are the most familiar form, where the numerator represents a part of the whole, and the denominator represents the total number of parts. Examples include 1/2, 3/4, 7/5, and -2/3.
- Decimal Numbers: These represent fractional parts of a whole using a decimal point. They can be terminating decimals, meaning they end at a specific point (like 0.5 or 2.75), or repeating decimals, meaning a pattern of digits repeats infinitely (like 0.333… or 1.666…).
The significance of Understanding Rational Numbers: A Real-World Example
These seemingly abstract concepts, rational numbers and integers, have practical applications in our everyday lives. Let’s say you’re baking a cake and the recipe calls for 1 1/2 cups of flour. This is a classic example of a mixed number, which combines an integer (1) and a fraction (1/2), and thus is a rational number but not an integer. You can’t measure out 1 1/2 cups of flour using only whole cups, you need a measurement that goes beyond the integer.
Similarly, think about your bank account. You might have a balance of $23.50. The decimal part, 0.50, represents a fraction of a dollar (half a dollar) and is a clear example of a rational number that is not an integer. Without understanding these concepts, managing your finances and completing everyday tasks would be significantly harder.
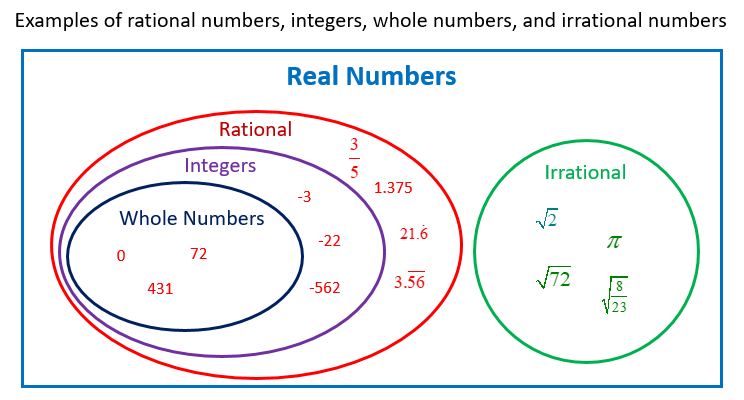
Image: www.onlinemathlearning.com
Exploring the Infinite Nature of Rational Numbers
The world of rational numbers is vast. Between any two integers, no matter how close together they may seem, there exists an infinite amount of rational numbers. Take the example of the numbers 1 and 2. There’s 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, and so on, not to mention all the fractions like 3/2, 5/4, 7/6, and countless others.
This infinite nature of rational numbers is what makes them so fascinating and also so challenging to quantify fully. It’s a testament to the complexity and endless possibility that lies within the seemingly simple realm of numbers.
Tips for Understanding and Utilizing Rational Numbers
Here are some tips for mastering the world of rational numbers, both integers and non-integers:
- Practice regularly: Regular practice with solving problems involving fractions, decimals, and mixed numbers will build your confidence and understanding.
- Visualize: Use diagrams, number lines, and real-life examples to create a visual representation of rational numbers, making them easier to grasp.
- Connect with real-world applications: Explore how rational numbers are utilized in various fields like cooking, finance, construction, and science, making the learning process more engaging and relevant.
- Embrace technology: Use online calculators, interactive simulations, and educational apps to explore and learn about rational numbers in a dynamic and interactive way.
By actively engaging with rational numbers and exploring their diverse applications, you’ll develop a deeper understanding of their significance in our world.
FAQ: Exploring Rational Numbers that are not Integers
Q1: Are all decimals rational numbers?
A: No, not all decimals are rational numbers. The decimal representation of an irrational number, such as pi, is infinite and non-repeating. This means it cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers, which is the defining characteristic of a rational number.
Q2: Why are rational numbers important in mathematics?
A: Rational numbers are the foundation of many mathematical concepts. They are used in algebra, geometry, calculus, and other advanced branches of mathematics. Understanding rational numbers is essential for solving equations, calculating measurements, and performing various mathematical computations.
Q3: Can a rational number be both an integer and a fraction?
A: Yes, an integer can be expressed as a fraction with a denominator of 1. For example, the integer 5 can also be written as the fraction 5/1. Therefore, a number can be both an integer and a fraction and still be considered a rational number.
There Are Rational Numbers That Are Not Integers
https://youtube.com/watch?v=BlDn2HFPYZU
Conclusion:
By understanding the world of rational numbers, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate nature of mathematics and its relevance in our everyday lives. Rational numbers are not just theoretical concepts; they are tools that we use to understand, quantify, and solve problems in various fields. We use rational numbers to measure ingredients in recipes, to manage financial budgets, to describe the world around us, and to explore complex mathematical concepts. So, the next time you encounter a fraction or a decimal, remember that it represents a rational number, a powerful tool in our mathematical toolbox.
Are you interested in delving further into the world of rational numbers? Let us know in the comments below!






