Have you ever wondered how refrigeration systems work their magic, keeping your food fresh and your drinks ice-cold? It’s all thanks to a complex interplay of pressure, temperature, and a special type of refrigerant: R407C. The heart of understanding this intricate process lies in a simple yet powerful tool: the R407C suction and discharge pressure chart. This chart serves as a vital guide for technicians, enabling them to diagnose potential issues and ensure optimal performance of refrigeration systems.

Image: theengineeringmindset.com
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of R407C and its pressure chart, unraveling its mysteries and empowering you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your refrigeration systems.
Understanding R407C: A Powerful Refrigerant
The refrigeration industry constantly evolves, seeking environmentally-friendly solutions while maintaining high performance. R407C, a blend of three different refrigerants (R32, R125, and R134a), emerged as a popular choice due to its compatibility with older R22 systems and its relatively low global warming potential.
R407C refrigerant, like many others, operates on the fundamental principle of heat transfer. Its journey from a low-pressure, low-temperature state to a high-pressure, high-temperature state allows it to absorb heat from the inside of your refrigerator and release it into the external environment. To properly manage this process, technicians rely heavily on the R407C suction and discharge pressure chart.
Deciphering the R407C Suction and Discharge Pressure Chart: A Deeper Look
The R407C suction and discharge pressure chart is a powerful tool that simplifies the complexities of refrigeration systems. It’s essentially a visual representation of how refrigerant pressure changes at various temperatures. This intricate relationship allows technicians to quickly assess the health and efficiency of a system just by measuring its pressures.
The Anatomy of the Chart
The chart typically features two main axes:
- Suction Pressure: This axis represents the pressure of the refrigerant as it enters the compressor. Lower suction pressures can indicate inadequate refrigerant charge or potential blockages in the system.
- Discharge Pressure: This axis depicts the pressure of the refrigerant as it exits the compressor. High discharge pressures can indicate problems with the compressor itself, an overcharge of refrigerant, or issues related to the condenser.
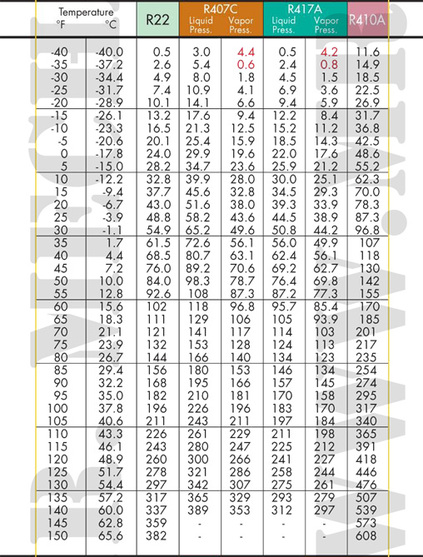
Image: brandonkss.github.io
Reading the Chart: A Guide to Performance
To utilize the chart effectively, technicians first measure the suction and discharge pressure of the refrigeration system. They then locate the intersection of these two pressure readings on the chart. This intersection point provides crucial information about the refrigerant temperature and its potential state.
For instance, if the pressure reading falls within the “optimal” zone, it suggests that the system is working efficiently and the refrigerant charge is appropriate. However, readings outside of this zone indicate potential problems that need further investigation.
The Importance of Accuracy and Caution
Interpreting the R407C suction and discharge pressure chart is a crucial skill for technicians, but it’s essential to remember that this chart is just a guide. It’s vital to consider other factors such as ambient temperature, condenser cleanliness, and even the age of the system. While the chart assists in diagnosing potential issues, a comprehensive analysis is essential for proper troubleshooting.
Beyond the Chart: Understanding the System as a Whole
The R407C suction and discharge pressure chart provides a valuable snapshot of the refrigeration system’s performance. However, it’s only one piece of the puzzle. To truly grasp the complexities of refrigeration and the role of R407C, it’s essential to understand the entire system and its components:
- Evaporator: This part absorbs heat from the refrigerated space, causing the refrigerant to evaporate and become a low-pressure gas. This is where the suction pressure is measured.
- Compressor: This component compresses the refrigerant gas, increasing its pressure and temperature. This is where the discharge pressure is measured.
- Condenser: The condenser releases heat from the compressed refrigerant gas, causing it to condense into a liquid.
- Expansion Valve: This valve regulates the flow of refrigerant, ensuring the appropriate pressure and temperature for the evaporator.
Understanding the interactions of these components with R407C and the information gleaned from the pressure chart allows technicians to pinpoint potential malfunctions and ensure optimal performance.
What the Chart can Tell You: Recognizing Common Issues
The R407C suction and discharge pressure chart can act as a powerful diagnostic tool, revealing signs of potential issues with various components:
- Low Suction Pressure:
- Refrigerant Leak: A leak in the system can lead to insufficient refrigerant charge, leading to low suction pressure.
- Compressor Issues: If the compressor is not operating efficiently, it can result in lower suction pressure.
- Dirty Evaporator: A dirty evaporator can impede heat transfer, resulting in low suction pressure.
- High Suction Pressure:
- Overcharge: Excess refrigerant can lead to high suction pressure.
- Expansion Valve Issues: A malfunctioning expansion valve can cause high suction pressure.
- Low Discharge Pressure:
- Compressor Issues: A failing compressor can lead to low discharge pressure.
- Dirty Condenser: A dirty condenser restricts heat transfer, resulting in lower discharge pressure.
It’s crucial to note that a combination of factors can contribute to pressure inconsistencies. Only a trained technician can accurately diagnose issues by analyzing the pressure readings in conjunction with other factors and utilizing the R407C suction and discharge pressure chart as a valuable guide.
Expert Tips for Refrigeration Maintenance
Maintaining the health of your refrigeration systems is crucial for optimal performance and energy efficiency. Here are some expert tips for keeping your equipment running smoothly:
- Regular Inspection and Maintenance: Regularly clean the condenser and evaporator coils. This prevents dust and dirt from accumulating, which reduces efficiency.
- Proper Refrigerant Charge: Ensure the system has the correct refrigerant charge. An undercharge or overcharge can significantly impact performance.
- Compressor Care: Monitor the compressor’s operating temperature and listen for unusual noises. Replacing the compressor is costly, so addressing issues early on is essential.
- Annual Check-Ups: Schedule annual service calls for a comprehensive inspection of your refrigeration system. This proactive approach can help identify potential problems before they become major issues.
R407c Suction And Discharge Pressure Chart
Conclusion: Empowering You with Knowledge
The R407C suction and discharge pressure chart is a valuable tool for technicians, enabling them to assess the health of refrigeration systems quickly and efficiently. By understanding the pressure readings and their implications, they can diagnose common issues and ensure optimal performance.
Armed with this knowledge, you can make informed decisions about your refrigeration systems, ensuring they operate efficiently and effectively. Remember, regular maintenance and proactive measures are key to extending the lifespan and performance of your equipment. Stay tuned, as we’ll delve deeper into the fascinating world of refrigeration and explore more valuable insights in our upcoming articles and resources!






